STAT 4830: Numerical Optimization for Data Science and Machine Learning - Damek Davis
STOCHASTIC GRADIENT DESCENT (SGD) CHEAT SHEET
GENERAL STOCHASTIC OPTIMIZATION PROBLEMS
Core Framework
- Empirical Risk: $L(w) = \frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^n \ell(w, x_i, y_i)$
- Full Gradient: $\nabla L(w) = \frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^n \nabla_w \ell(w, x_i, y_i)$
- Unbiased Mini-batch Gradient:
Key Problem Examples
Linear Regression
- Model: $f_w(x) = w^T x + b$
- Loss: $\ell(w, x_i, y_i) = \frac{1}{2}(w^T x_i - y_i)^2$
- Gradient: $\nabla_w \ell = (w^T x_i - y_i)x_i$
Logistic Regression
- Model: $P(y=1|x) = \sigma(w^T x)$
- Loss: $-y_i \log(\sigma(w^T x_i)) - (1-y_i) \log(1-\sigma(w^T x_i))$
- Gradient: $(\sigma(w^T x_i) - y_i)x_i$
Neural Networks
- Model: $f_w(x) = f_L(f_{L-1}(…f_1(x; w_1)…; w_{L-1}); w_L)$
- Loss: Task-dependent
- Gradient: Via backpropagation
Empirical vs. Population Risk
- Empirical Risk: $L_{\text{emp}}(w) = \frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^n \ell(w, x_i, y_i)$ (training data)
- Population Risk: $L_{\text{pop}}(w) = \mathbb{E}_{(x,y) \sim \mathcal{D}}[\ell(w, x, y)]$ (all possible data)
- Generalization Bound: $L_{\text{pop}}(w) \leq L_{\text{emp}}(w) + \mathcal{O}\left(\sqrt{\frac{\text{complexity}(w) + \log(1/\delta)}{n}}\right)$
- SGD Insight: Can provide implicit regularization beyond empirical risk minimization
SGD METHODS AND VARIANTS
Gradient Methods Spectrum
Full Gradient Descent (GD)
- Batch Size: $n$ (entire dataset)
- Per-step Cost: $O(n m)$
- Gradient Variance: Zero
- Steady-State Error: Zero (with $\alpha$ small enough)
Mini-batch SGD
- Batch Size: $b$ (subset)
- Per-step Cost: $O(bm)$
- Gradient Variance: $O(1/b)$
- Steady-State Error: $O(\sqrt{\alpha/b})$
Pure SGD
- Batch Size: 1 (single example)
- Per-step Cost: $O(m)$
- Gradient Variance: $O(1)$
- Steady-State Error: $O(\sqrt{\alpha})$
Sampling Strategies
- With Replacement: Each example equally likely to appear in each batch (theoretical)
-
Without Replacement (Epoch-based): Shuffle entire dataset once per epoch, then process in batches (practical)
# Each epoch: 1. Generate random permutation π of indices {1,2,...,n} 2. Create batches: B₁={π(1),...,π(b)}, B₂={π(b+1),...,π(2b)},... 3. Process all batches sequentially
SGD Variants
Momentum
- Update Rule:
- $m_{k+1} = \beta m_k + g(w_k)$
- $w_{k+1} = w_k - \alpha m_{k+1}$
- Effect on Init Error: Reduces by accelerating convergence
- Effect on Steady-State: Increases by factor $\frac{1+\beta}{1-\beta}$
- Best Batch Size: Large
Exponential Moving Average (EMA)
- Update Rule:
- $w_{k+1} = w_k - \alpha g(w_k)$
- $\tilde{w}_{k+1} = \gamma \tilde{w}_k + (1-\gamma) w_{k+1}$
- Effect on Init Error: Minimal effect
- Effect on Steady-State: Reduces significantly
- Best Batch Size: Small
Preconditioning
- Update Rule: $w_{k+1} = w_k - \alpha P^{-1} g(w_k)$
- Effect on Init Error: Reduces by balancing convergence rates
- Effect on Steady-State: Increases, especially in low-curvature dimensions
- Best Batch Size: Large
Weight Decay
- Modified Objective: $L_{\text{wd}}(w) = L(w) + \frac{\lambda}{2}|w|_2^2$
- Gradient Modification: $\nabla L_{\text{wd}}(w) = \nabla L(w) + \lambda w$
- Update Rule: $w_{k+1} = (1 - \alpha\lambda)w_k - \alpha \nabla L(w_k)$
- Effect on NQM: Improves condition number from $\frac{h_1}{h_2}$ to $\frac{h_1 + \lambda}{h_2 + \lambda}$
- Typical Values: $\lambda \in [10^{-5}, 10^{-3}]$
Learning Rate Schedules
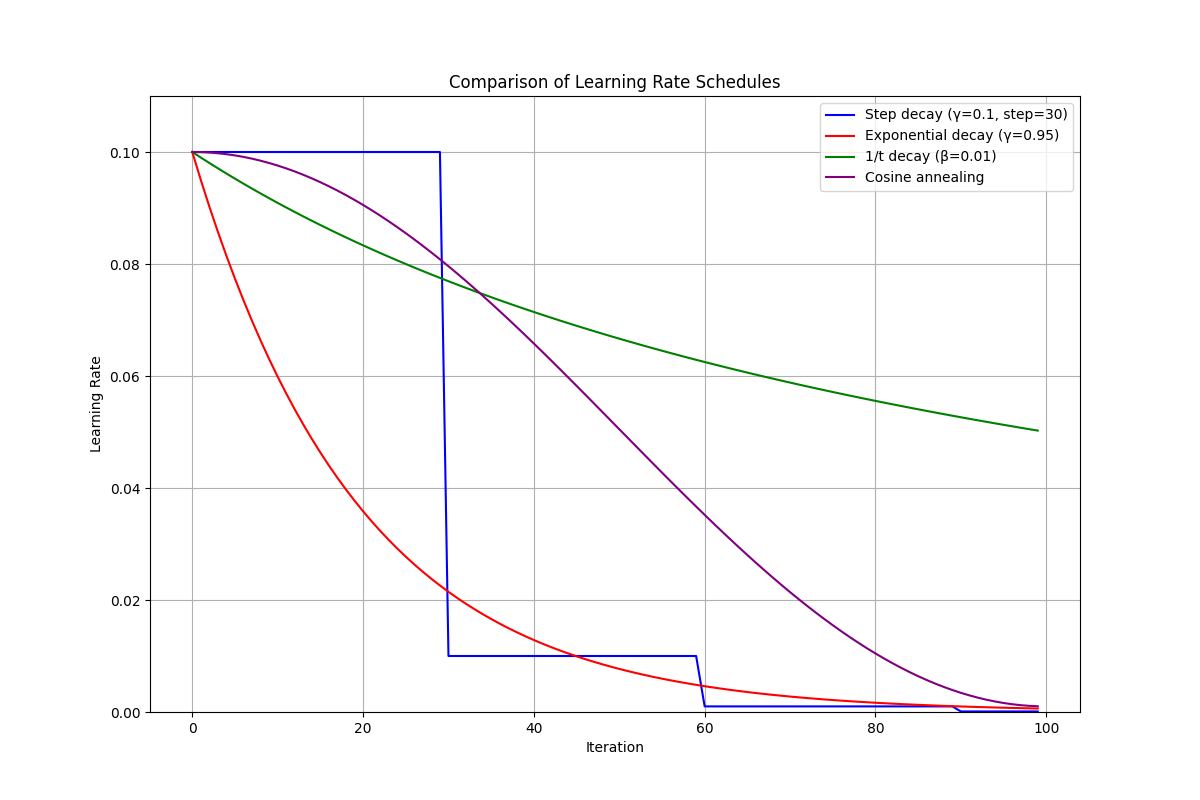
Step Decay
- Formula: $\alpha_k = \alpha_0 \cdot \gamma^{\lfloor k/s \rfloor}$
- Properties: Discrete drops at regular intervals
Exponential Decay
- Formula: $\alpha_k = \alpha_0 \cdot \gamma^k$
- Properties: Smooth continuous decrease
1/t Decay
- Formula: $\alpha_k = \frac{\alpha_0}{1 + \beta k}$
- Properties: Theoretical convergence guarantees
Cosine Annealing
- Formula: $\alpha_k = \alpha_{\min} + \frac{1}{2}(\alpha_0 - \alpha_{\min})(1 + \cos(\frac{k\pi}{K}))$
- Properties: Smooth, non-monotonic decay
PYTORCH IMPLEMENTATION
Complete Training Loop
SGD TRAINING LOOP IN PYTORCH
============================
EPOCH LOOP +-------------------------------------------------------------+
| |
v |
+-------------+ |
| DATASET | +------------------------+ |
| | | DATALOADER | |
| [x₁,y₁] +------->| for batch_x, batch_y | |
| [x₂,y₂] | | in dataloader: | |
| [x₃,y₃] | +------------------------+ |
| ... | | |
+-------------+ | SAMPLING |
| (w/ or w/o replacement) |
v |
+-------------------+ +------------------+ |
| 5. PARAM UPDATE | | MINI-BATCH | |
| | | [x₂,y₂] | |
| optimizer.step() | | [x₇,y₇] SHUFFLE | |
| | | [x₄,y₄] ↺↺↺↺↺↺ | |
| w ← w - α∇L | +------------------+ |
| | | |
| LEARNING RATE | | |
| SCHEDULER | v |
| scheduler.step() | +------------------+ |
| | | ZERO GRADIENTS | |
+-------------------+ | optimizer. | |
^ | zero_grad() | |
| +------------------+ |
| | |
| v |
| +------------------+ +---------------+
| | 1. FORWARD PASS | | |
| | | | |
| | outputs = model( | | |
| | batch_x) | | |
| | | | |
| | nn.Module | | |
| +------------------+ | |
| | | |
| | ŷ (predictions) | |
| v | |
+-------------------+ +------------------+ | |
| 4. BACKWARD PASS | | 2. LOSS CALC | | |
| | | | | |
| loss.backward() | | loss = F.mse_ | | |
| | | loss(ŷ, batch_y)| | |
| Creates: | | | | |
| param.grad | | + λ||w||² (decay)| | |
| | +------------------+ | |
| | | | |
| | | scalar loss | |
| | v | |
+-------------------+ +------------------+ | |
^ | 3. COMPUTATIONAL | | |
| | GRAPH | | |
| | | | |
| | (autograd builds | | |
+--------------------+ differentiation +--------+ |
| pathway) | |
+------------------+ |
Data Loading
# Dataset definition
class SimpleDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, features, labels):
self.features = features
self.labels = labels
def __len__(self): return len(self.features)
def __getitem__(self, idx): return self.features[idx], self.labels[idx]
# DataLoader without replacement (default)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=32, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)
# DataLoader with replacement
sampler = RandomSampler(dataset, replacement=True, num_samples=len(dataset))
dataloader_with_replacement = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=32, sampler=sampler)
Model Definition
# Model definition
class LinearRegression(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim):
super().__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(input_dim, 1) # creates weight and bias
def forward(self, x):
return self.linear(x) # computes x @ weights.T + bias
# Loss computation
predictions = model(features)
loss = F.mse_loss(predictions, targets) # Mean squared error
loss_binary = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(predictions, targets)
Optimizer Configuration
# Basic SGD
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
# SGD with momentum
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, momentum=0.9)
# SGD with weight decay
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, weight_decay=1e-4)
# SGD with momentum and weight decay
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=1e-4)
Learning Rate Schedulers
# Step LR: drops by factor gamma every step_size epochs
scheduler = StepLR(optimizer, step_size=30, gamma=0.1)
# Exponential decay: multiplies by gamma each epoch
scheduler = ExponentialLR(optimizer, gamma=0.95)
# Cosine annealing: follows cosine curve over T_max epochs
scheduler = CosineAnnealingLR(optimizer, T_max=100)
# 1/t decay: learning rate decays proportionally to 1/t
scheduler = LambdaLR(optimizer, lr_lambda=lambda epoch: 1.0 / (1.0 + beta * epoch))
# Reduce on plateau: reduces when metric stops improving
scheduler = ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer, mode='min', factor=0.1, patience=10)
Complete Training Loop
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# Training loop
for batch_features, batch_labels in dataloader:
# Zero gradients
optimizer.zero_grad()
# Forward pass
outputs = model(batch_features)
loss = F.mse_loss(outputs, batch_labels)
# Backward pass
loss.backward()
# Update parameters
optimizer.step()
# Update learning rate
scheduler.step() # or scheduler.step(val_loss) for ReduceLROnPlateau
ADVANCED TECHNIQUES
Implementing EMA
# Manual implementation
def update_ema(model, ema_model, decay=0.999):
with torch.no_grad():
for param, ema_param in zip(model.parameters(), ema_model.parameters()):
ema_param.data = decay * ema_param.data + (1 - decay) * param.data
# Using PyTorch utilities
from torch.optim.swa_utils import AveragedModel
ema_model = AveragedModel(model, avg_fn=lambda avg_param, param, num_averaged:
0.999 * avg_param + (1 - 0.999) * param)
# Update in training loop
ema_model.update_parameters(model)
Mixing Techniques
- Implementation Strategy: Add components incrementally, validate each addition
- Common Combinations:
- Large batch: Momentum + Scheduling + (Preconditioning)
- Small batch: EMA + Scheduling + Weight Decay
- Hyperparameter Interactions:
- Adding momentum often requires reducing learning rate
- Weight decay may need recalibration when used with momentum
Minimal Working Example
You can test out the code in the notebook.
Key Takeaways
- SGD with constant learning rate converges to a “noise ball” around the optimum
- Batch size trades off per-iteration cost vs. gradient precision
- Momentum accelerates convergence but amplifies steady-state noise
- EMA reduces steady-state noise without affecting convergence rate
- Weight decay improves conditioning and provides regularization
- Learning rate schedules balance fast initial progress with precise final convergence
- Combining techniques requires careful hyperparameter tuning